Easy Teacher Worksheetscom Nouns Cut Out the Noun Tiles at
Nouns are words that are a part of speech that we use to people, places, and things. This word form is essential for communication to identify the subject of any sentence. These worksheets include activities that involve writing the correct plurals of given nouns, turning nouns into possessives, identifying all forms within a given list of words, differentiating between abstract and concrete (people/places/things), the use of correct capitalization, creating original sentences using specific types of words as prompted, using picture prompts to write original sentences, and more. The writing kids work on with the topic the better! Fun Project Idea: Have your students perform the Schoolhouse Rock "Nouns" song (available on YouTube) for extra reinforcement? They are a solid classroom aid.
Get Free Worksheets In Your Inbox!
Print Noun Worksheets
Click the buttons to print each worksheet and associated answer key.

Common Nouns
These are people, places, or things kids see just about every day of their life.


Plural Form
Circle the correct plural form of each word. Complete each sentence by writing the plural form that are found in parentheses.



Singular Possessive Form
Add an apostrophe and an "s" to the end of a singular noun to make it possessive. Possessives are used to show that something belongs to a person, place, thing or idea.
![]()
![]()

Identifying Them
Circle just about everything that is a person/people, place, or thing.
![]()
![]()

Concrete Forms
These are a person, place or thing that can be perceived by the senses. You know that a word is concrete if you can see, hear, feel, touch, smell or taste the thing it stands for. For each abstract noun given below, write a related concrete noun that might be used to suggest the abstract idea. The first one has been done for you.
![]()
![]()
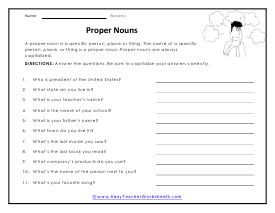
Proper Nouns
These designate a specific person, place or thing. They are always capitalized. Answer the questions. Be sure to capitalize your answers correctly.
![]()
![]()

Common and/or Proper
Common are generally a person, place or thing, as a result they do not need to be capitalized. Propers are specific people, places or things. Propers always begin with capital letters.
![]()
![]()

All About Nouns
Write original sentences that satisfy each prompt that you are given.
![]()
![]()

Concrete Like A Rock
Reach sentence. Write the word in the correct columns. Color in the blocks that contain concrete word forms.
![]()
![]()

Plurals
You can make most singular words plural by adding -s to the end. For words ending in x, z, s, sh and ch, add -es to the end to create the plural. Add an -s or -es at the end of each word to form the plural.
![]()
![]()
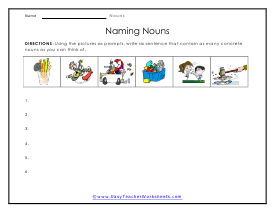
Naming Things
Using the pictures as prompts, write six sentence that contain as many concrete words as you can think of.
![]()
![]()

Make More!
Change the singular form into the plural form to complete each sentence.
![]()
![]()

Is That Proper or Common?
Determine whether each word is a common or a proper. If the word is common, write common on the line. If the word is proper, write it on the line, correcting the capitalization.
![]()
![]()
How to Position Nouns in Sentences
A noun is a word that refers to a person, a place, or a thing. Ruth Bader Ginsburg, Louvre, and spaceship are all examples of nouns. They can be used to define inert objects, farseeing concepts, and a wild number of different pursuits. To pluralize them we normally just add an -s to the end of the word. If the word already ends in -s we often add an -es to form a plural. The common form of these words are used to define nonspecific things. The proper form is used to define specific things. The abstract form is used to define things that we cannot use our senses on. You can also use the collective form to describe groups.
Positioning a Noun in a Sentence
When used in a sentence, the position of a noun determines its function within that sentence. It may be used as a subject, direct object, an indirect object, or even as the object of a preposition.
In total, there are seven positions a noun can take in a sentence. They are explained below with examples.
1. Subject
A noun that comes before the verb in a sentence is usually the subject.
Examples:
- The doctor wrote him a prescription.
- Sara sang a song at the wedding.
2. Direct Object
A noun following an action verb in a sentence is usually a direct object. The direct object can be identified by asking what or whom questions.
Examples:
- The girl played the violin.
- Mrs. Kim sold the antique table.
- The senior management commended Alison.
Mrs. Kim sold what? Answer: The antique table. Antique table is the direct object of the verb sold.
The senior management commended whom? Answer: Alison. Alison is the direct object of the verb commended.
There's an exception to this rule. When the subject does not perform an action to a noun in the sentence, or when no noun receives the action.
3. Indirect Object
A noun preceding the direct object in a sentence is called an indirect object. An indirect object can be identified by asking to what, for what, or to whom, and for whom questions.
- Allen sent his mother a china dish.
- The class can buy the headmaster a new telescope.
- Nina got her daughter an umbrella.
In the first sentence, Allen sent the china dish to whom? Answer: Mother. Mother is the indirect object. In the next sentence, the class can buy the telescope for whom? Answer: Headmaster. The headmaster is the indirect object.
4. Subject Complement
A noun following a verb of being is usually a subject complement.
Examples:
- My presence alone is a gift.
- Logan is a detective.
- Amanda will be fine.
5. Object of Preposition
Nouns following a preposition are called the object of the preposition. Every preposition has an object; usually, that object comes first after the preposition and the last in the prepositional phrase.
Examples:
- The hills are across the forest.
- She took her daughters to school.
- After dinner, the kids went to bed
In the first sentence, the preposition is across, and forest is the noun or object of that preposition. In the next sentence, the preposition is to, and the object of that preposition is the noun school.
6. Appositive Nouns
Appositive means near. Appositive nouns are usually present in the middle of a sentence but they can also be located anywhere in the sentence except the beginning. They are typically placed near another noun or pronoun, set off by commas. They enhance our understanding of the original noun or pronoun.
Examples:
- Noah, my brother is a drummer.
- My uncle, Jim, is here for the wedding.
- Sanvi, my childhood friend, just visited Australia.
In the first sentence, my brother is the subject, and Noah is the appositive. Uncle is the subject of the second sentence, and Jim is the appositive.
7. Predicate Noun
Predicate nouns follow a linking verb that stands for the subject. A predicate noun can also be known as an alternate word for the sentence's subject.
Examples:
- I am Superman.
- Katherine will be president.
- He was late.
In the first sentence I is the subject, and Superman is the predicate noun. In the next sentence, the subject is Katherine, and the predicate noun is President.
Source: https://www.easyteacherworksheets.com/langarts/partsofspeech-nouns.html
0 Response to "Easy Teacher Worksheetscom Nouns Cut Out the Noun Tiles at"
Postar um comentário